
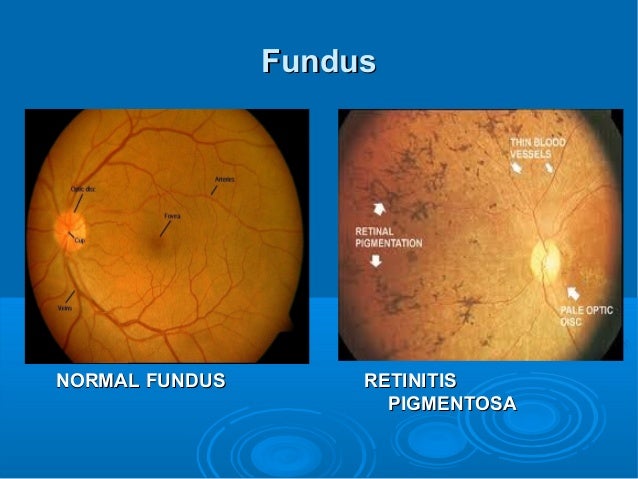
A clinical study found that fundus autofluorescence (FAF) imaging indicated disrupted lipofuscin in the RPE as well as abnormalities in the photoreceptor layer.

With regard to the photoreceptor segments, the IZ band has been found to be absent in the region of EZ band abnormalities, which suggests that the EZ band was longer than the IZ band. Rod photoreceptor death is followed by degeneration of the RPE cells and eventually leads to the loss of the cones. In RP, the photoreceptor lines are shortened with the degeneration of photoreceptors. So the three highly reflective lines are the ELM, EZ, and IZ from the inner to the outer retina, which are commonly used to evaluate the integrity of the photoreceptor segments. The 18 zones progressing from the innermost to the outermost layers of the retina are listed in numerical order in table 1, and the detailed structural layers are shown in the pictures captured by OCT (fig. The second and third outer retinal hyperreflective bands were termed the ‘ellipsoid zone' and the ‘interdigitation zone'. So experts in retinal imaging have defined a consensus for OCT imaging terminology. Another hyperreflective region (the third outer retinal hyperreflective band) known as the cone outer segment tips (COST) line was represented to be the interdigitation of the apical processes of the RPE with the cone outer segments. The hyperreflective region was confirmed to be the ellipsoid portion of the inner segments, which was packed with mitochondria. However, the connecting cilium between the inner and outer photoreceptor segments is a loose collection of microtubules, which does not correspond to the hyperreflective region. The hyperreflective region (the second outer retinal hyperreflective band) between the inner and outer photoreceptor segments was known as IS/OS line. Since the earliest histopathological changes are the shortening of the photoreceptor segments, the integrity of the photoreceptor lines has been widely studied. Cones comprise 5% of the photoreceptors, which are distributed throughout the fovea, and the density decreases in the perifoveal area. In human eyes, rods account for 95% of the photoreceptors, which are absent at the fovea but peak in the zone about 20° outside of the fovea.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
